



Overview of Perplexity
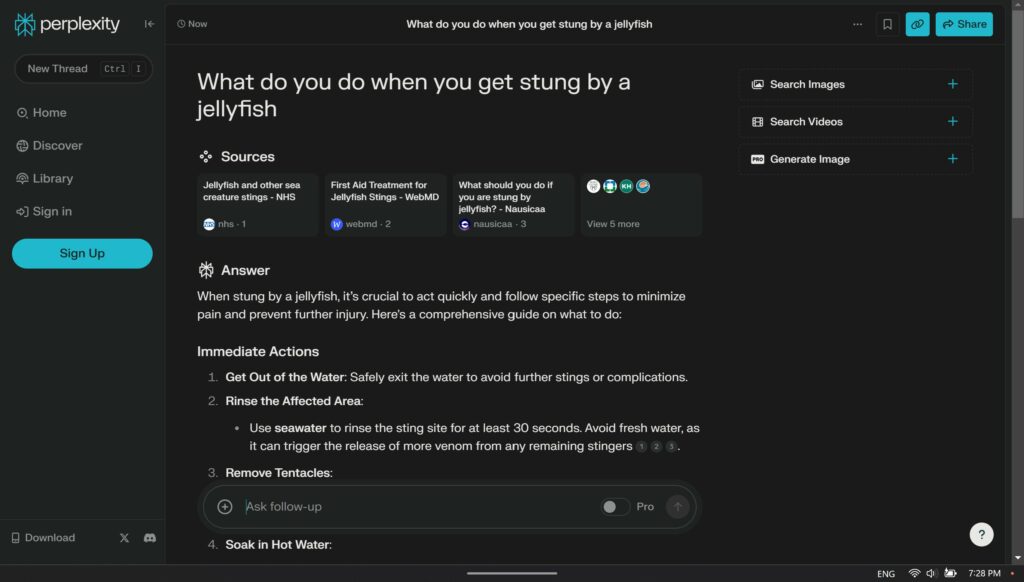
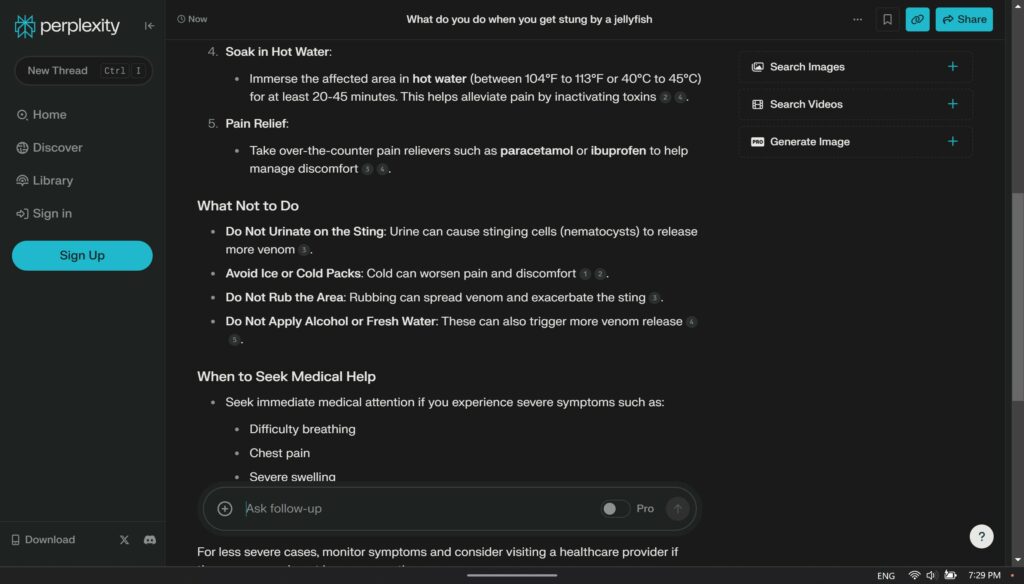
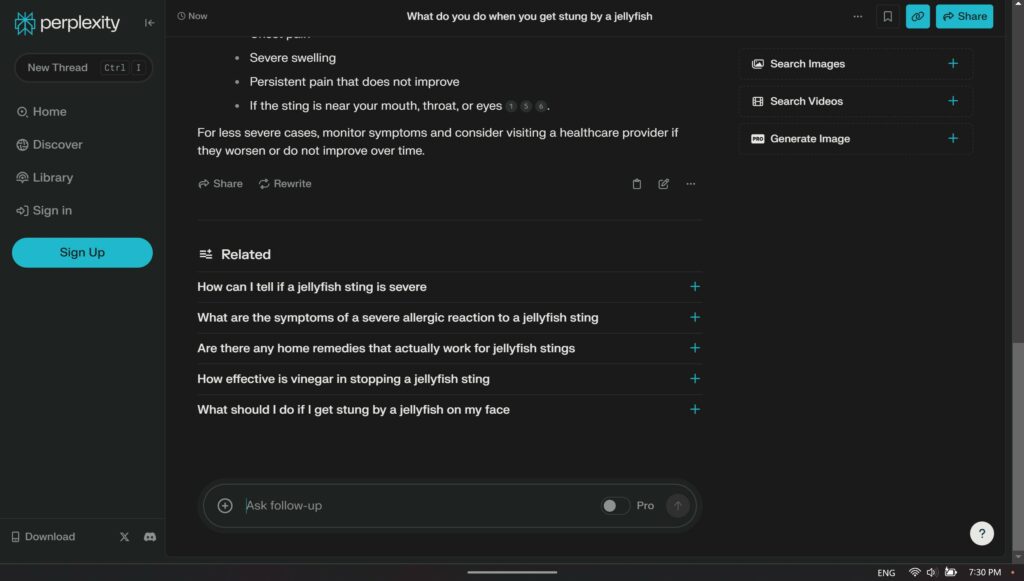
For module 2 blog i chose to use Perplexity. I have never heard or seen this AI tool before so I was curious about it. I have used other LLMs before like ChatGPT for statistic courses, suggestions and other things. Perplexity is very similar to ChatGPT in the sense that it searches the internet to give as accurate as possible answers to prompts.
What I noticed about Perplexity is the easy to use interface, it looks more inviting than ChatGPT. I also noticed with the prompt I imputed it gave a more detailed response and delivered it in a nice readable way instead of just a block of answers. I found that it would go the extra mile to provide extra information that can be helpful even though it is not directly related to the question. This can be very helpful when doing research, or being used in educational settings.
TPAK Analysis of Perplexity’s Function – Prompted from ChatGPT
Perplexity.ai fits the TPACK framework by blending technology, pedagogy, and content. It offers a tool that can enhance learning if used correctly:
In conclusion, Perplexity.ai is a powerful tool that, when integrated thoughtfully, can enhance teaching and learning experiences. Educators must, however, ensure it is used in a way that encourages deeper thinking, accurate content comprehension, and technology literacy, ensuring a balance among technological, pedagogical, and content knowledge to meet educational goals.
References
“create a TPACK analysis of perplexity.ai AI search engine functions” prompt ChatGPT, 11 Oct. 2024, OpenAI, https://chatgpt.com/.
Famure, Princess. Screenshot of Perplexity.ai interface. 11 Oct. 2024. Author’s personal photos.
Mayer’s Cognitive Theory of Multimedia Learning, developed by psychologist Richard E. Mayer, explains how people learn more effectively from multimedia presentations, which combine text, images, audio, and animations.
The principles that seemed most intuitive to me was the signaling principle; which involves using headings and visual cues to direct attention to key elements. It naturally guides the learner to focus on important information, reducing cognitive strain. The principle that surprised me the most was modality principle, the suggestion that narration combined with images is more effective than labels with images was surprising. It challenges the common assumption that written text is essential for reinforcement.
In my screencasting video, I explain how to create a simple menu poster using CapCut software and how it can be used for other purposes other than video editing. I integrated coherence Principle aiming to keep my screencast free of unnecessary distractions and focused on the key learning points.
When making my video, my main focus was was an audience new to capcut, I focused on simplifying complex concepts (managing Intrinsic Load) and pacing the material to make it digestible. For example, breaking down ideas into manageable chunks (Segmenting).
In the past i have implemented the redundancy principle trying to avoid overwhelming learners by not repeating information in both text and narration in past presentations. I am however guilty of the modality principle overusing text on slides alongside narration, potentially overloading the verbal channel. Going off of that, I would try and focus on leveraging modality more effectively by integrating narration with visuals and minimizing text. Additionally, try to explore how personalization can make your multimedia more engaging and learner-friendly.